- News
- 0 likes
- 22718 views
- 0 comments
Dear Colleagues!
I invite you to my training "Theory and Practice of A-PRF, I-PRF, PRGF, PRJF, and PRJEF: Preparation Protocols for Dentists, Cosmetologists, Orthopedists, Traumatologists, Surgeons, and Other Specialists Interested in Gel-Free Plasma Preparation Technologies. How to Prepare High-Quality PRF Clots." Now, PRF preparation is done in syringes. No tubes required!
If you have chosen the Dr. Renat Akhmerov® A-PRF, I-PRF, PRGF, PRJF, or PRJEF therapy technologies, don't rush to buy special tubes. After watching my video below, you'll see that you won’t need to purchase expensive tubes for A-PRF, I-PRF, PRGF, PRJF, and PRJEF in the future. Regular syringes will work just fine.
Every successful specialist should have the right tools that make it easier for modern doctors to reach new heights of professional perfection. Mastering innovative techniques (including PRF) has become more and more a matter of prestige for any respected specialist.
PRF (Platelet Rich Fibrin) refers to platelet-enriched fibrin, which is obtained by centrifugation from the patient’s own blood. Essentially, PRF is a clot of blood plasma without red blood cells. The centrifugation procedure is carried out directly in the doctor's office.
For example, what is the area of PRF application in dentistry?
The main indications for using PRF clots are:
- sinus lifting procedures;
- bone and soft tissue augmentation surgeries;
- addressing periodontal issues;
- post-extraction patient care;
- accelerating gum and skin wound healing.
How does PRF work?
Over the course of a week, active substances such as the following are slowly released from the PRF clot:
| Leukocytes | by intensively stimulating progenitor cells, contribute to bone synthesis and induce the transformation of monocytes into macrophages |
| VEGF | a signaling protein, also known as vascular endothelial growth factor, which stimulates vasculogenesis and angiogenesis |
| PDGF | a protein that is a platelet-derived growth factor, essential for angiogenesis |
| TGF-beta | a protein known as transforming growth factor beta, which regulates proliferation, cell differentiation, and many other cellular functions |
| Proteins | important for angiogenesis and tissue growth stimulation |
| TSP | as a powerful inhibitor of angiogenesis, thrombospondin influences endothelial cell growth and adhesion |
| IGF-1 | a protein known as insulin-like growth factor-1 |
| BMP-2 and BMP-7 | a complex of bone morphogenetic proteins that act on osteoblasts, osteoclasts, chondroblasts, and chondrocytes, promoting their proliferation and differentiation, ultimately leading to intense bone growth |
What are the types of PRF?
There are 5 basic types of PRF. Let's take a closer look at them, as well as other similar techniques.
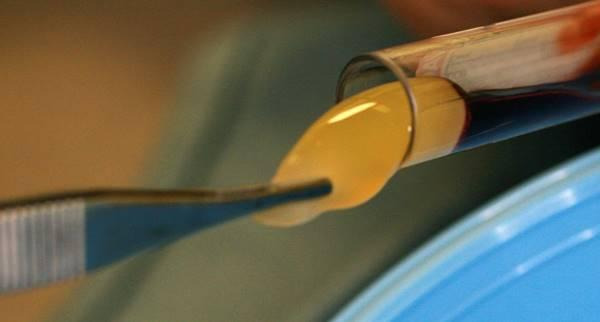
RF – standard fibrin clot, successfully used in dental practice for over 15 years. To prepare it, 20.0 ml syringes are required. The centrifugation time is 8-12 minutes (in a centrifuge at a speed of 3000 rpm).
No test tubes are needed. The clot is obtained in 20 ml syringes.
A-PRF (advanced) – this type of fibrin clot is obtained in about 15 minutes at a speed of 2000 rpm (in our centrifuge). A lower centrifugation speed helps achieve a higher concentration of growth factors in the clot, with a more even distribution. It should be noted that due to individual blood properties, this centrifugation speed in some patients may cause a decrease in ESR. In this case, the fibrin clot may form before the erythrocytes are fully settled, leading to the presence of erythrocyte impurities in the clot.
No test tubes are needed. The clot is obtained in 20 ml syringes.
-PRF (injectable PRF) – blood serum (after centrifugation), which transforms into a clot, is centrifuged in 20.0 ml syringes. Our centrifuge requires 3 minutes at a speed of 1500 rpm for this. During this time, part of the erythrocytes, which are in the upper part of the test tube, settles, but the plasma does not thicken. This plasma is used to obtain i-PRF for injections. The thickening time is around 10 minutes (in pure form), or about 4 minutes (when PRF clot is added).
Sticky bone – almost identical to i-PRF, but this Japanese technique does not use a plasma activator in the test tube, and the centrifugation is done in the usual PRF mode. The result is plasma without impurities, thickening exclusively due to the fibrin present in it, so it takes longer to thicken than with an activator.
No test tubes are needed. The clot is obtained in 20 ml syringes.
What tools are needed to work with PRF?
PRF Centrifuge. This is needed primarily. It is necessary to have an angle of 90 degrees.
Video on the PRF clot preparation process:
What is the fundamental difference between the mentioned technologies A-PRF, I-PRF, PRF, etc. and PRP PLASMOLIFTING?
In that, PRP Plasmolifting uses plasma containing leukocytes and platelets, whose kinins and other biologically active substances initiate tissue regeneration. This happens due to the presence of an anticoagulant and targeted blood filtration.
In A-PRF, I-PRF, PRF, etc. technologies, no anticoagulant is added, and the preparations contain only fibrin enriched with platelets. They actively affect bone tissue as "templates" for new cell growth.

Comments (0)